Join
When you have a geographical dataset and a tabular dataset that share a common field, you can join them to add the columns of the tabular dataset to the geographical dataset.
This association is made possible by matching the identifier values found in the geographic dataset with those found in the data table.
This operation is called a “join” (also used in GIS software or database management systems) and is performed here simply by choosing the name of the column containing identifier values in the dataset and in the geographic layer.
To ensure that this method works properly, the values taken by the identifiers, on the one hand for the geographic layer and on the other for the tabular dataset, must be unique.
Theoretical example
Example of attributes in a geographical dataset:
| id | name |
|---|---|
| BE | Belgium |
| DE | Deutschland |
| FR | France |
| LU | Luxembourg |
| NL | Nederland |
Example of attributes in a tabular dataset:
| id_country | pop_density |
|---|---|
| DE | 231.5 |
| LU | 218.9 |
| NL | 432.0 |
| FR | 118.6 |
| BE | 373.1 |
By joining the tabular dataset to the geographical dataset using the id column of the geographical dataset and the id_country column of the tabular dataset, we obtain the following dataset:
| id | name | pop_density |
|---|---|---|
| BE | Belgium | 373.1 |
| DE | Deutschland | 231.5 |
| FR | France | 118.6 |
| LU | Luxembourg | 218.9 |
| NL | Nederland | 432.0 |
The geographical dataset now contains the population density values from the tabular dataset, allowing for a cartographic representation of this value.
Accessing the join functionality
To access the join functionality, you must first have added a geographic dataset and a tabular dataset.
Then, in the Layer Manager, click on the “Join” button located on the tabular dataset to be joined to a geographic dataset.
 Join button in the Layer Manager
Join button in the Layer ManagerParameters
In Magrit, the join is done from the tabular dataset to be joined to a geographical dataset. It is mandatory to fill in the following parameters:
- The geographical layer to which to join the data,
- The column of the geographical layer containing the identifier values,
- The column of the tabular dataset containing the identifier values.
It is also possible to set the following optional parameters:
- Non-case-sensitive identifier values,
- Disregard diacritics, spaces and hyphens in identifier values,
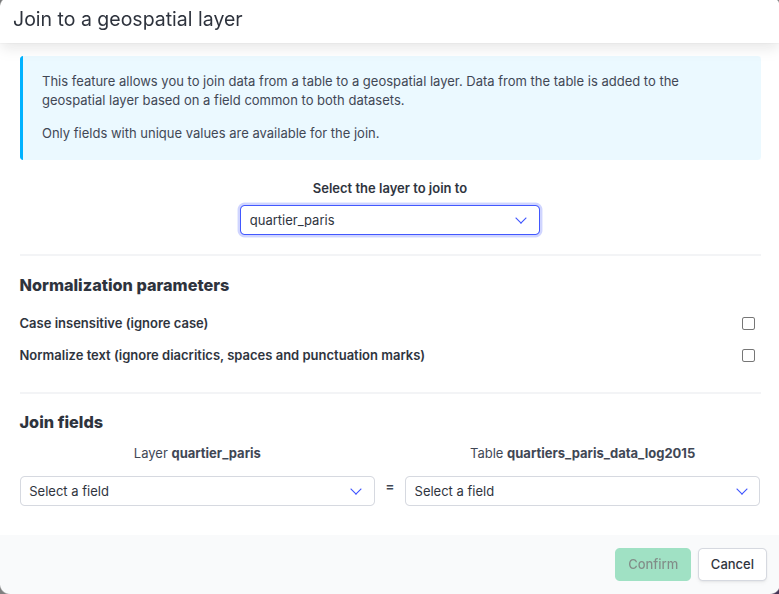 Join modal window before selecting identifier fields
Join modal window before selecting identifier fieldsBased on this information, the correspondences between the identifier values of the two datasets are established.
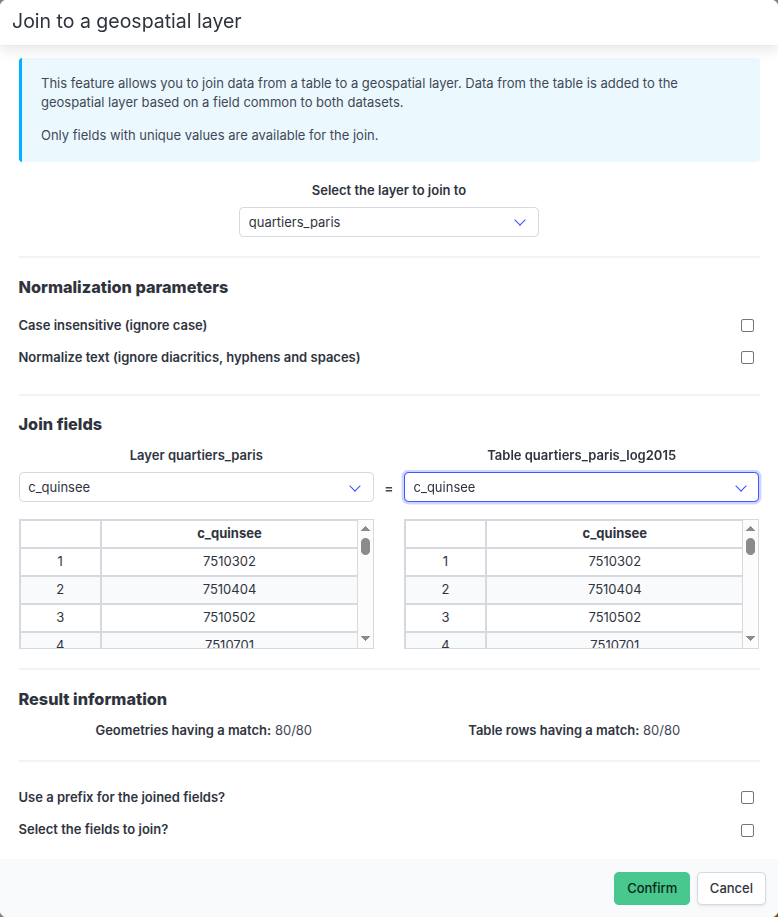
Displaying the columns used for the join and results
A data table is displayed under the dropdown menu of the geographic layer and tabular dataset identifier fields.
This table displays the row number and identifier value of the two columns used for the join.
Entries with unique matches are displayed without colors (these are valid matches for the join).
If entries have multiple matches, they are displayed in red (which prevents the join from being performed). If entries have no matches or are empty, they are displayed in orange. Entries displayed in red or orange are moved to the top of the table for easing their identification.
Results
If no matches are found (or if multiple matches are found, i.e. if several ID values in the geographic dataset match the same ID value in the tabular dataset, or vice versa), the join cannot be performed.
 Join modal window (no matches found)
Join modal window (no matches found)If one or more matches are found, the tabular data can be added to the corresponding entities of the geographical layer, based on the following options:
- Possibility to select the columns to add to the geographical layer,
- Possibility to add a prefix to the added columns,
- Possibility to remove the entities from the geographical layer for which no correspondence has been found.
A summary section displays the number of matches found in the geographic layer and in the tabular dataset (as well as the number of empty entries, if any).
 Join modal window
Join modal window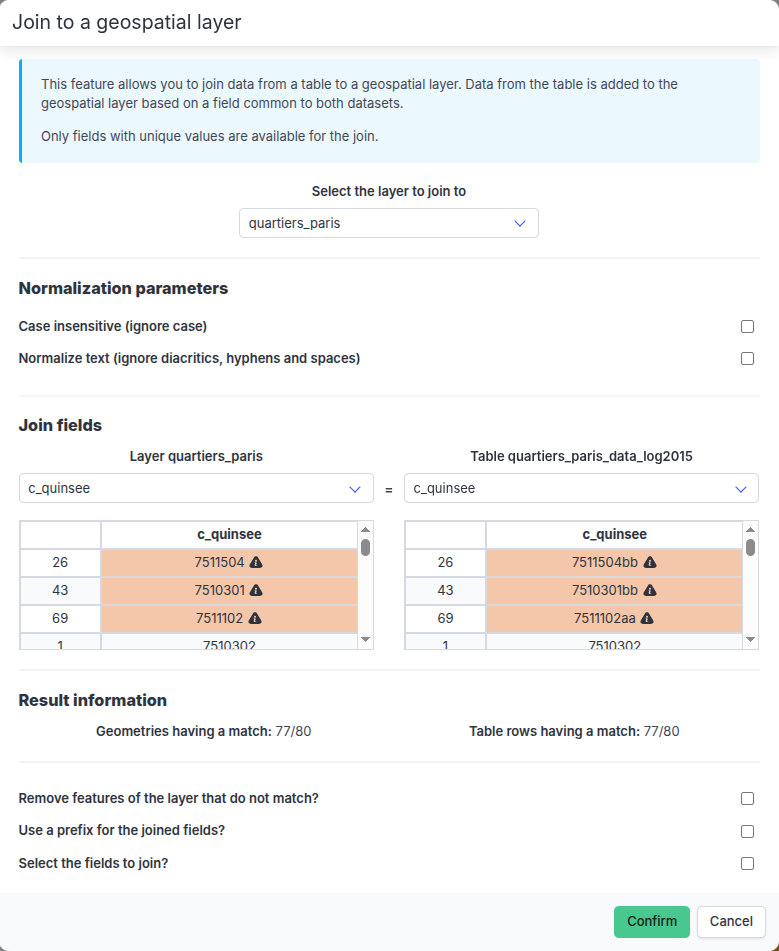 Join modal window (with unmatched entities)
Join modal window (with unmatched entities)